Metal finishing uses a variety of materials and processes to coat, color and/or plate metallic and non-metallic substrate surfaces to create desired surface characteristics (examples of which include improving appearance, abrasion resistance or corrosion resistance). Typical supporting processes can include degreasing, cleaning, pickling, etching and/or polishing.
Chemicals and materials used in metal finishing include solvents, detergents and surfactants for cleaning; acids and bases for cleaning, etching and activating; and solutions of metal salts for depositing the finish onto the substrate. Two of the most common metal finishing processes are cadmium cyanide electroplating and hexavalent chromium conversion coating.

Cadmium Cyanide Electroplating
Cadmium cyanide plating is used for corrosion inhibition on many critical metal components. High purity deionized (DI) water is typically used for rinse water and process bath makeup for this process. Rinsewaters from cadmium cyanide plating require treatment and the residuals (ion exchange media or sludge) are regulated as RCRA hazardous waste (D003, D006, F006).
Hexavalent Chromium Conversion Coating
Hexavalent chromium (Cr+6) conversion coating is used for corrosion inhibition on aluminum structures and components. High purity deionized (DI) water is also used for rinse water and process bath makeup for this process. Rinsewaters from hexavalent chromium conversion coating require treatment and the treatment residuals (ion exchange media or sludge) are regulated as RCRA hazardous waste (D007, F019).
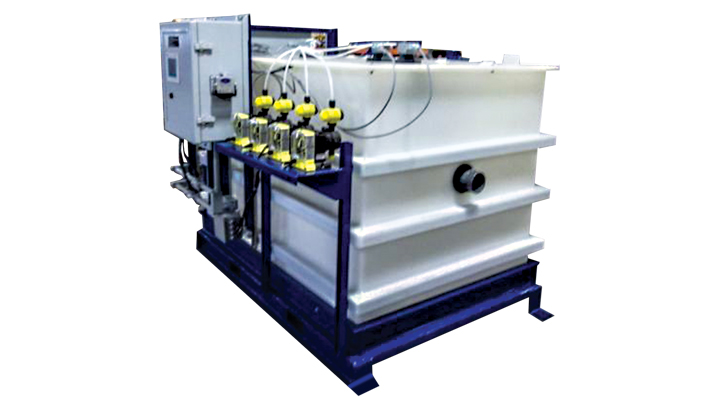
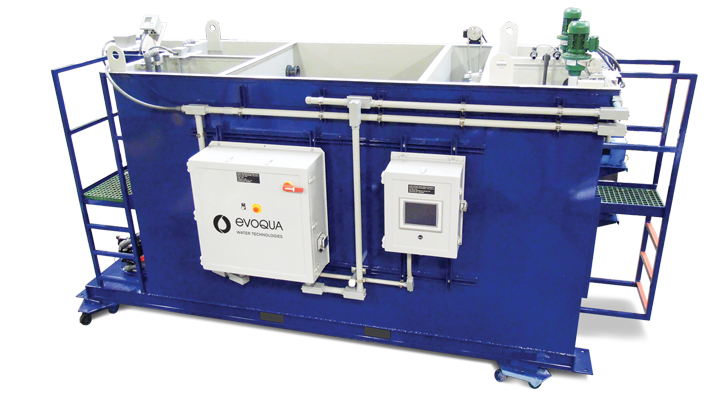
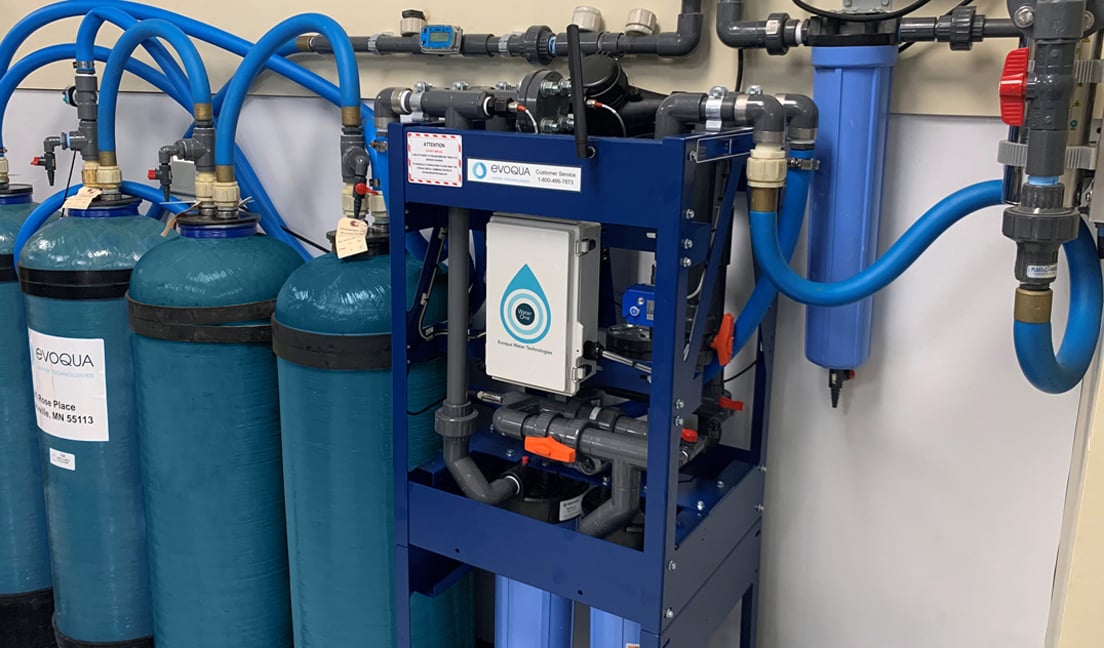
Wastewater Treatment Solutions
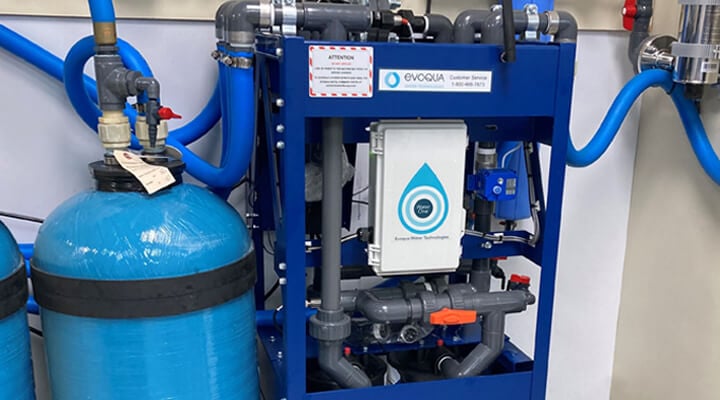
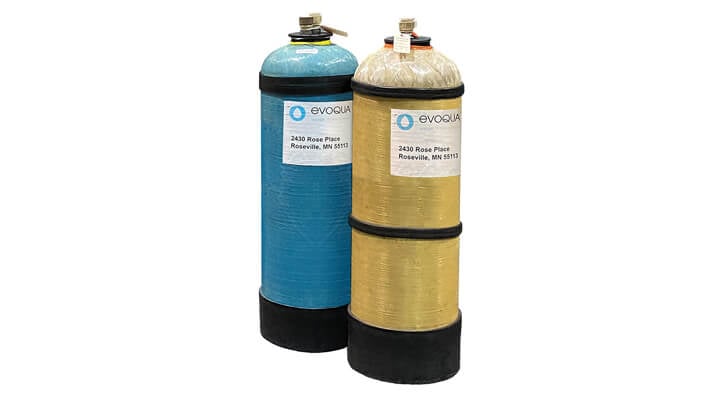
Evoqua’s wastewater ion exchange systems and capital equipment are used to remove the hazardous components, allowing the treated rinse water to either be recycled back to the rinse baths or discharged to the POTW. The contaminant-laden ion exchange media is shipped back to Evoqua’s owned and operated RCRA treatment facility for compliant processing which epitomizes the “cradle to grave” waste treatment approach.